AWS ALB Ingress Service - Basics ¶
Step-01: Introduction ¶
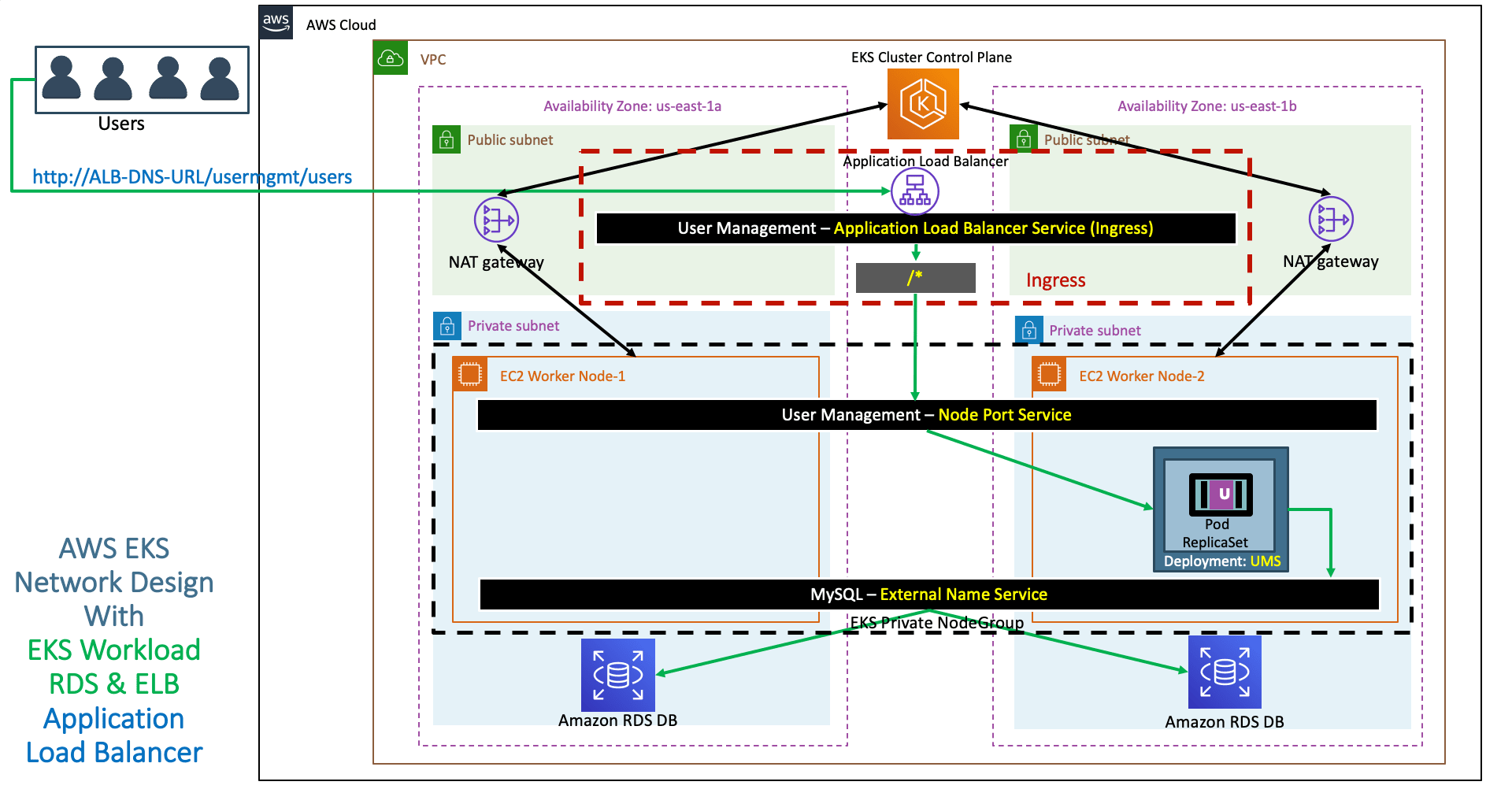
- Discuss about the Application Architecture which we are going to deploy
- Refer Presentation from slide 106 onwards
Kubernetes Manifests ¶
#01-MySQL-externalName-Service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: usermgmtdb.cxojydmxwly6.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com
#02-UserManagementMicroservice-Deployment-Service.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: usermgmt-microservice
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
spec:
initContainers:
- name: init-db
image: busybox:1.31
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo -e "Checking for the availability of MySQL Server deployment"; while ! nc -z mysql 3306; do sleep 1; printf "-"; done; echo -e " >> MySQL DB Server has started";']
containers:
- name: usermgmt-restapp
image: stacksimplify/kube-usermanagement-microservice:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8095
env:
- name: DB_HOSTNAME
value: "mysql"
- name: DB_PORT
value: "3306"
- name: DB_NAME
value: "usermgmt"
- name: DB_USERNAME
value: "dbadmin" # RDS DB Username is dbadmin
- name: DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-db-password
key: db-password
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- nc -z localhost 8095
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /usermgmt/health-status
port: 8095
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
#03-Kubernetes-Secrets.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-db-password
type: Opaque
data:
db-password: ZGJwYXNzd29yZDEx
#04-UserManagement-NodePort-Service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: usermgmt-restapp
ports:
- port: 8095
targetPort: 8095
#nodePort: 31231
#05-ALB-Ingress-Basic.yml
# Annotations Reference: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
annotations:
# Ingress Core Settings
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "alb"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
# Health Check Settings
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: traffic-port
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: '15'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: '5'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: '200'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count: '2'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count: '2'
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service
servicePort: 8095
Step-02: Foundation Section ¶
Create ALB Manually for additional understanding ¶
- Create a simple Application Load Balancer and understand the following
- Application Load Balancer Core Concepts
- ALB should be Internet facing or Internal
- Listeners (Default HTTP 80)
- Rules (HTTP /*)
- Target Groups
- Targets (Backends)
- HealthCheck Settings
- Protocol: HTTP
- Traffic Port (8095)
- Health Check Path: /usermgmt/health-status
- Success Codes: 200
- Health check many other settins
- Delete the Load Balancer
Understand about ALB Ingress Annotations ¶
- Understand about ALB Ingress Annotations
- Reference: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/
Best Selling AWS EKS Kubernetes Course on Udemy ¶
- Absolute practical scenarios required for real-time implementations
- 18 AWS Services covered in combination with AWS EKS
- 31 Kubernetes Concepts covered in combination with AWS EKS & AWS Services
- Step by Step Documentation on Github and Website
- 18 Docker Images available on Docker Hub for implementing practical scenarios

Step-03: Create ALB kubernetes basic Ingress Manifest ¶
- Create a basic ALB Ingress template
- 05-ALB-Ingress-Basic.yml
# Annotations Reference: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/ apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service labels: app: usermgmt-restapp annotations: # Ingress Core Settings kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "alb" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing # Health Check Settings alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTP alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: traffic-port alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: '15' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: '5' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: '200' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count: '2' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count: '2' spec: rules: - http: paths: - path: /* backend: serviceName: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service servicePort: 8095
Step-04: Deploy Application with ALB Ingress Template included ¶
# Deploy Application with ALB Template
kubectl apply -f kube-manifests/
# Verify our UMS App is UP and Running
kubectl get pods
kubectl logs -f <pod-name>
kubectl logs -f usermgmt-microservice-5c89458797-xsb64
# Get List of Ingress (Make a note of Address field)
kubectl get ingress
# List Services
kubectl get svc
# Describe Ingress Controller
kubectl describe ingress ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service
# Verify ALB Ingress Controller logs
kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get po -n kube-system | egrep -o 'alb-ingress-controller-[A-Za-z0-9-]+') -n kube-system
- We should not see anything like below log in ALB Ingress Controller log, if we see we did something wrong with ALB Ingress Controleer deployment primarily in creating IAM Policy, Service Account & Role and Associating Role to Service Account.
07:28:39.900001 1 controller.go:217] kubebuilder/controller "msg"="Reconciler error" "error"="failed to build LoadBalancer configuration due to unable to fetch subnets. Error: WebIdentityErr: failed to retrieve credentials\ncaused by: AccessDenied: Not authorized to perform sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity\n\tstatus code: 403, request id: 3d54741a-4b85-4025-ad11-73d4a3661d09" "controller"="alb-ingress-controller" "request"={"Namespace":"default","Name":"ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service"}
Step-05: Verify the ALB in AWS Management Console & Access Application using ALB DNS URL ¶
- Verify Load Balancer
- In Listeners Tab, click on View/Edit Rules under Rules
- Verify Target Groups
- GroupD Details
- Targets: Ensure they are healthy
- Access Application
http://<ALB-DNS-URL>/usermgmt/health-status
Step-06: Clean Up ¶
kubectl delete -f kube-manifests/
How ALB Ingress Controller Works? ¶
AWS ALB Ingress Installation ¶
AWS ALB Ingress Implementation Basics ¶
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel