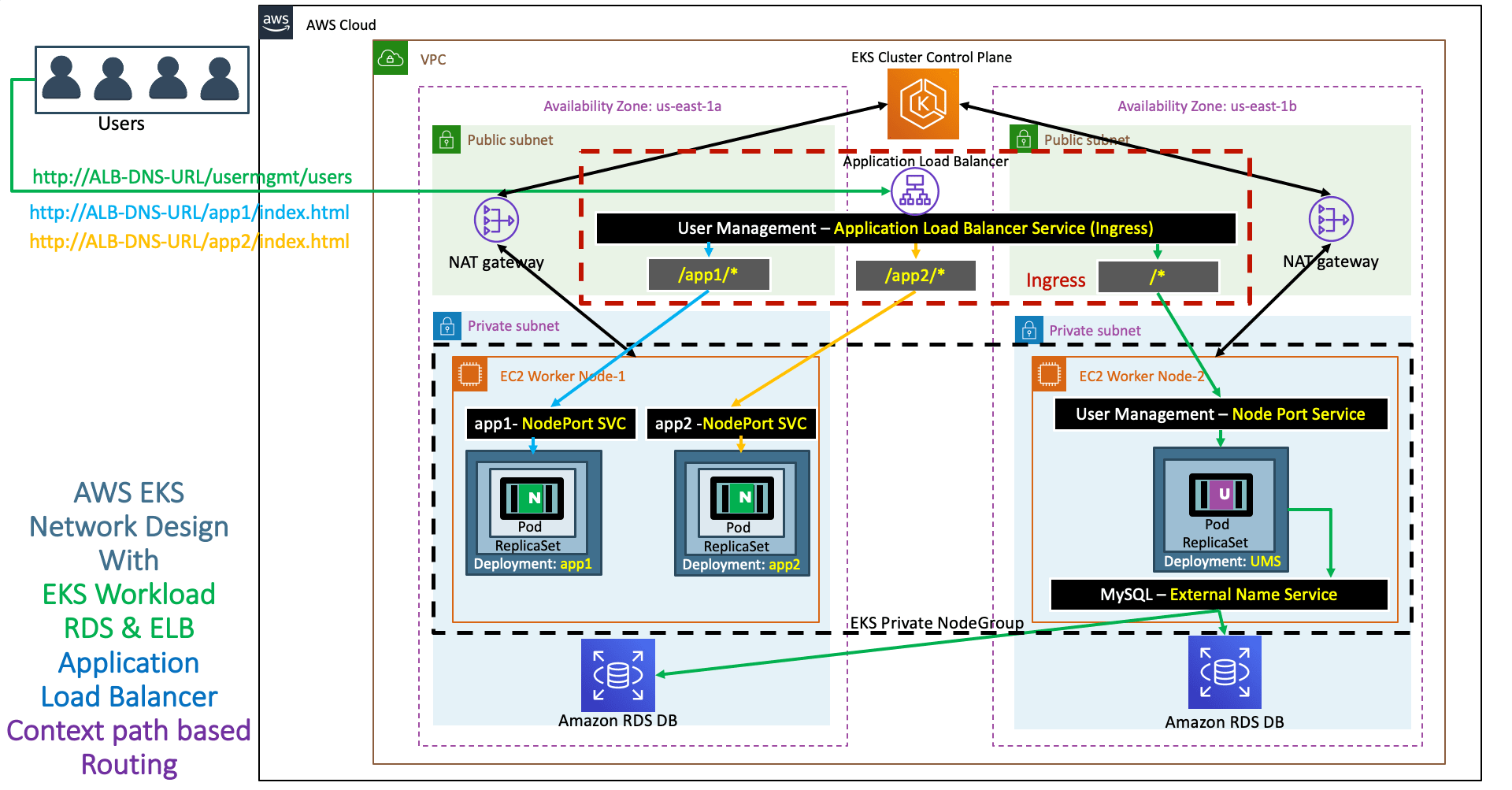
AWS ALB Ingress Service - Context Path Based Routing ¶
Step-01: Introduction ¶
- Discuss about the Architecture we are going to build as part of this Section
- We are going to create two more apps with static pages in addition to UMS.
- App1 with context as /app1 - Simple Nginx custom built image
- App2 with context as /app2 - Simple Nginx custom built image
- We are going to deploy all these 3 apps in kubernetes with context path based routing enabled in Ingress Controller
- /app1/* - should go to app1-nginx-nodeport-service
- /app2/* - should go to app1-nginx-nodeport-service
- /* - should go to sermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service
- As part of this process, this respective annotation
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-statuswill be moved to respective application NodePort Service. Only generic settings will be present in Ingress manifest annotations area07-ALB-Ingress-ContextPath-Based-Routing.yml - Refer Presentation from slide 106 onwards
Kubernetes Manifests ¶
#01-MySQL-externalName-Service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: usermgmtdb.cxojydmxwly6.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com
#02-UserManagementMicroservice-Deployment-Service.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: usermgmt-microservice
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
spec:
initContainers:
- name: init-db
image: busybox:1.31
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo -e "Checking for the availability of MySQL Server deployment"; while ! nc -z mysql 3306; do sleep 1; printf "-"; done; echo -e " >> MySQL DB Server has started";']
containers:
- name: usermgmt-restapp
image: stacksimplify/kube-usermanagement-microservice:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8095
env:
- name: DB_HOSTNAME
value: "mysql"
- name: DB_PORT
value: "3306"
- name: DB_NAME
value: "usermgmt"
- name: DB_USERNAME
value: "dbadmin" # RDS DB Username is dbadmin
- name: DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-db-password
key: db-password
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- nc -z localhost 8095
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /usermgmt/health-status
port: 8095
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 10
#03-Kubernetes-Secrets.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-db-password
type: Opaque
data:
db-password: ZGJwYXNzd29yZDEx
#04-UserManagement-NodePort-Service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
annotations:
#Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: usermgmt-restapp
ports:
- port: 8095
targetPort: 8095
#05-Nginx-App1-Deployment-and-NodePortService.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: app1-nginx-deployment
labels:
app: app1-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: app1-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: app1-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: app1-nginx
image: stacksimplify/kube-nginxapp1:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: app1-nginx-nodeport-service
labels:
app: app1-nginx
annotations:
#Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /app1/index.html
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: app1-nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
#06-Nginx-App2-Deployment-and-NodePortService.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: app2-nginx-deployment
labels:
app: app2-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: app2-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: app2-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: app2-nginx
image: stacksimplify/kube-nginxapp2:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: app2-nginx-nodeport-service
labels:
app: app2-nginx
annotations:
#Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /app2/index.html
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: app2-nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
#07-ALB-Ingress-ContextPath-Based-Routing.yml
# Annotations Reference: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service
labels:
app: usermgmt-restapp
annotations:
# Ingress Core Settings
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "alb"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
# Health Check Settings
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: traffic-port
#Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer
#alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: '15'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: '5'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: '200'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count: '2'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count: '2'
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /app1/*
backend:
serviceName: app1-nginx-nodeport-service
servicePort: 80
- path: /app2/*
backend:
serviceName: app2-nginx-nodeport-service
servicePort: 80
- path: /*
backend:
serviceName: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service
servicePort: 8095
# Important Note-1: In path based routing order is very important, if we are going to use "/*", try to use it at the end of all rules.
Step-02: Create Nginx App1 & App2 Deployment & Service ¶
- App1 Nginx: 05-Nginx-App1-Deployment-and-NodePortService.yml
- App2 Nginx: 06-Nginx-App2-Deployment-and-NodePortService.yml
Best Selling AWS EKS Kubernetes Course on Udemy ¶
- Absolute practical scenarios required for real-time implementations
- 18 AWS Services covered in combination with AWS EKS
- 31 Kubernetes Concepts covered in combination with AWS EKS & AWS Services
- Step by Step Documentation on Github and Website
- 18 Docker Images available on Docker Hub for implementing practical scenarios

Step-03: Update Health Check Path Annotation in User Management Node Port Service ¶
- Health check path annotation should be moved to respective node port services if we have to route to multiple targets using single load balancer.
- 04-UserManagement-NodePort-Service.yml
#Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status
Step-04: Create ALB Ingress Context path based Routing Kubernetes manifest ¶
- 07-ALB-Ingress-ContextPath-Based-Routing.yml
# Annotations Reference: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-alb-ingress-controller/guide/ingress/annotation/ apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service labels: app: usermgmt-restapp annotations: # Ingress Core Settings kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "alb" alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing # Health Check Settings alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-protocol: HTTP alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-port: traffic-port #Important Note: Need to add health check path annotations in service level if we are planning to use multiple targets in a load balancer #alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /usermgmt/health-status alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-interval-seconds: '15' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-timeout-seconds: '5' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/success-codes: '200' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthy-threshold-count: '2' alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/unhealthy-threshold-count: '2' spec: rules: - http: paths: - path: /app1/* backend: serviceName: app1-nginx-nodeport-service servicePort: 80 - path: /app2/* backend: serviceName: app2-nginx-nodeport-service servicePort: 80 - path: /* backend: serviceName: usermgmt-restapp-nodeport-service servicePort: 8095 # Important Note-1: In path based routing order is very important, if we are going to use "/*", try to use it at the end of all rules.
How ALB Ingress Controller Works? ¶
AWS ALB Ingress Installation ¶
AWS ALB Ingress Implementation Basics ¶
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel
Step-05: Deploy all manifests and test ¶
- Deploy
kubectl apply -f kube-manifests/ - Verify ingress resource got created
# List Ingress Load Balancers kubectl get ingress # List Pods kubectl get pods # List Services kubectl get svc -
Verify ALB Ingress Controller Logs
# Verify logs kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get po -n kube-system | egrep -o 'alb-ingress-controller-[A-Za-z0-9-]+') -n kube-system -
We should not see anything like below log in ALB Ingress Controller, if we see we did something wrong with ALB Ingress Controleer deployment primarily in creating IAM Policy, Service Account & Role and Associating Role to Service Account.
07:28:39.900001 1 controller.go:217] kubebuilder/controller "msg"="Reconciler error" "error"="failed to build LoadBalancer configuration due to unable to fetch subnets. Error: WebIdentityErr: failed to retrieve credentials\ncaused by: AccessDenied: Not authorized to perform sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity\n\tstatus code: 403, request id: 3d54741a-4b85-4025-ad11-73d4a3661d09" "controller"="alb-ingress-controller" "request"={"Namespace":"default","Name":"ingress-usermgmt-restapp-service"}
- Access Application
http://<ALB-DNS-URL>/app1/index.html http://<ALB-DNS-URL>/app2/index.html http://<ALB-DNS-URL>/usermgmt/health-status
Step-06: Clean Up ¶
kubectl delete -f kube-manifests/