EKS - Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA)
Step-01: Introduction
- What is Horizontal Pod Autoscaling?
- How HPA Works?
- How HPA configured?
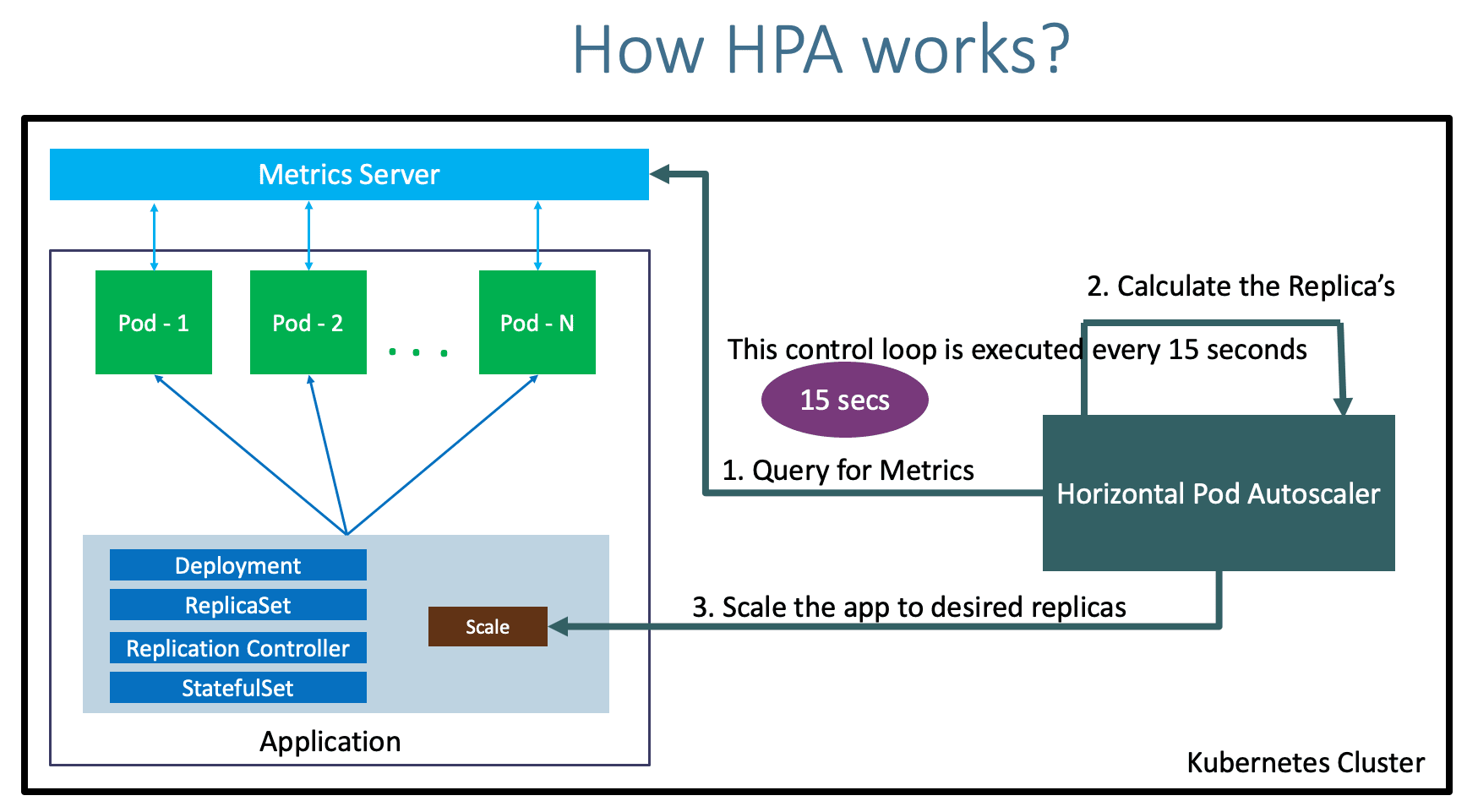
Step-02: Install Metrics Server
# Verify if Metrics Server already Installed
kubectl -n kube-system get deployment/metrics-server
# Install Metrics Server
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.3.6/components.yaml
# Verify
kubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-system
Step-03: Review Deploy our Application
# Deploy
kubectl apply -f kube-manifests/
# List Pods, Deploy & Service
kubectl get pod,svc,deploy
# Access Application (Only if our Cluster is Public Subnet)
kubectl get nodes -o wide
http://<Worker-Node-Public-IP>:31231
Kubernetes Manifets
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpa-demo-deployment
labels:
app: hpa-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hpa-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hpa-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: hpa-nginx
image: stacksimplify/kubenginx:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "100m"
limits:
memory: "500Mi"
cpu: "200m"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpa-demo-service-nginx
labels:
app: hpa-nginx
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: hpa-nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 3123
Step-04: Create a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler resource for the "hpa-demo-deployment"
- This command creates an autoscaler that targets 50 percent CPU utilization for the deployment, with a minimum of one pod and a maximum of ten pods.
- When the average CPU load is below 50 percent, the autoscaler tries to reduce the number of pods in the deployment, to a minimum of one.
- When the load is greater than 50 percent, the autoscaler tries to increase the number of pods in the deployment, up to a maximum of ten
# Template
kubectl autoscale deployment <deployment-name> --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
# Replace
kubectl autoscale deployment hpa-demo-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
# Describe HPA
kubectl describe hpa/hpa-demo-deployment
# List HPA
kubectl get horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/hpa-demo-deployment
Step-05: Create the load & Verify how HPA is working
# Generate Load
kubectl run --generator=run-pod/v1 apache-bench -i --tty --rm --image=httpd -- ab -n 500000 -c 1000 http://hpa-demo-service-nginx.default.svc.cluster.local/
# List all HPA
kubectl get hpa
# List specific HPA
kubectl get hpa hpa-demo-deployment
# Describe HPA
kubectl describe hpa/hpa-demo-deployment
# List Pods
kubectl get pods
Step-06: Cooldown / Scaledown
- Default cooldown period is 5 minutes.
- Once CPU utilization of pods is less than 50%, it will starting terminating pods and will reach to minimum 1 pod as configured.
Step-07: Clean-Up
# Delete HPA
kubectl delete hpa hpa-demo-deployment
# Delete Deployment & Service
kubectl delete -f kube-manifests/
AWS EKS - Elastic Kubernetes Service - Masterclass

Step-08: Imperative vs Declarative for HPA
- From Kubernetes v1.18 onwards, we have a declarative way of defining HPA policies using
behavior object in yaml.
- Support for configurable scaling behavior
- Starting from v1.18 the v2beta2 API allows scaling behavior to be configured through the HPA behavior field.
- Behaviors are specified separately for scaling up and down in scaleUp or scaleDown section under the behavior field
behavior:
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
- type: Pods
value: 4
periodSeconds: 15
selectPolicy: Max
- Reference: Select V1.18 from top right corner on Kubernetes website for V1.18 documentation
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/
Referencess
Metrics Server Releases
- https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling - Scale based on many type of metrics
- https://v1-16.docs.kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale-walkthrough/

